尽量说人话
二叉树
模板
递归
traverse(root) {
// 前序遍历
traverse(root.left)
// 中序遍历
traverse(root.right)
// 后序遍历
}
迭代
const res = []
const stack = []
root && stack.push(root)
while (stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop()
if (node == null) {
res.push(stack.pop().val)
continue
}
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right) // 右
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left) // 左
stack.push(node) // 中
stack.push(null)
}
return res
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
层序遍历的关键是用一个数组保存上一层的节点,需要注意在遍历这个保存节点的数组时,注意缓存长度,因为遍历过程中数组长度会变化(js 中普通 for 循环数组长度变化会影响遍历范围)
var levelOrder = function (root) {
const res = []
if (root == null) {
return res
}
const q = [root]
while (q.length) {
const len = q.length // 注意缓存长度,因为遍历过程中数组长度会变化
const path = []
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const node = q.shift()
path.push(node.val)
if (node.left) q.push(node.left)
if (node.right) q.push(node.right)
}
res.push(path)
}
return res
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度
递归
先确定好函数的返回值,树的深度。
终止条件是什么?root == null时,返回深度为 0
递推条件:左右子树深度的最大值加上 1
var maxDepth = function (root) {
if (root == null) return 0
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1
}
112. 路径总和
递归
递归的基本思想,确定好函数要返回什么,然后从结束条件开始思考
这里我们需要返回的是是否有一条路径的值加起来等于 targetSum
结束条件是:
root 为 null,返回
false到叶子节点了,返回
targetSum === root.val
然后思考递推关系,去掉一个节点之后,左右子树只要有一条可以走通就行,那么用||,并且 targetSum 需要减去root.val
var hasPathSum = function (root, targetSum) {
if (root === null) {
return false
}
if (root.left === null && root.right === null) {
return targetSum === root.val
}
return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val)
}
129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
DFS
用 preSum 记录之前的总和,记得到叶子节点(root.left == null && root.right == null)的时候就应该返回sum,不然结果会变成 2 倍
const dfs = (root, prevSum) => {
if (root === null) {
return 0
}
const sum = prevSum * 10 + root.val
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return sum
} else {
return dfs(root.left, sum) + dfs(root.right, sum)
}
}
var sumNumbers = function (root) {
return dfs(root, 0)
}
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
我们需要首先找到root在中序数组中的位置,来分割左子树和右子树
而前序数组的第一个值就是root,所以遍历中序数组找到root即可(这里可以用 map 保存中序数组中每个值的位置来优化)
然后我们就需要根据中序数组root的位置来分割左子树和右子树

var buildTree = function (preorder, inorder) {
// slice 切分数组 速度较慢
// if (preorder.length === 0) return null
// const rootValue = preorder[0]
// const index = inorder.indexOf(rootValue)
// const left = buildTree(preorder.slice(1, index + 1), inorder.slice(0, index))
// const right = buildTree(preorder.slice(index + 1), inorder.slice(index + 1))
// const root = new TreeNode(rootValue, left, right)
const hash = new Map()
for (let i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
hash.set(inorder[i], i)
}
return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, hash)
}
function build(preorder, p_start, p_end, inorder, i_start, i_end, hash) {
if (p_start > p_end) {
return null
}
const rootVal = preorder[p_start]
const index = hash.get(rootVal)
const leftChild = index - i_start
const root = new TreeNode(rootVal)
root.left = build(preorder, p_start + 1, p_start + leftChild, inorder, i_start, index - 1, hash)
root.right = build(preorder, p_start + leftChild + 1, p_end, inorder, index + 1, i_end, hash)
return root
}
199. 二叉树的右视图
DFS
var rightSideView = function (root) {
const res = []
dfs(root, res, 0)
return res
}
function dfs(root, res, depth) {
if (root == null) {
return
}
if (depth == res.length) {
// 如果当前节点所在深度还没有出现在res里,说明在该深度下当前节点是第一个被访问的节点,因此将当前节点加入res中。
res.push(root.val)
}
depth++
dfs(root.right, res, depth)
dfs(root.left, res, depth)
}
BFS
var rightSideView = function (root) {
if (root == null) return []
let path = [root]
const res = []
while (path.length) {
const len = path.length
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const node = path.shift()
if (node.left) path.push(node.left)
if (node.right) path.push(node.right)
if (i === len - 1) res.push(node.val)
}
}
return res
}
链表
141. 环形链表
快慢指针
我们设置两个指针分别从head出发,每次走一步;另一个从head.next出发,每次走两步,如果最后相交(相等),就说明链表有环
注意循环的条件是p2 && p2.next
var hasCycle = function (head) {
if (!head || !head.next) {
return false
}
let p1 = head
let p2 = head.next
while (p2 && p2.next) {
if (p1 === p2) {
return true
}
p1 = p1.next
p2 = p2.next.next
}
return false
}
206. 反转链表
递归
使用递归,我们需要先明确三点:递归函数的输出、输出和递归函数的终止条件
把整个函数当做一个递归函数来看
首先是第一点,我们输入的是头结点 head
那么第二点,输出就是反转之后的链表的头节点,就叫last好了
最后是第三点,什么时候/条件结束?这个一下子想不出来也没关系,我们先来想想递归的过程应该是怎么样的?
开始递归
const last = reverseList(head.next)
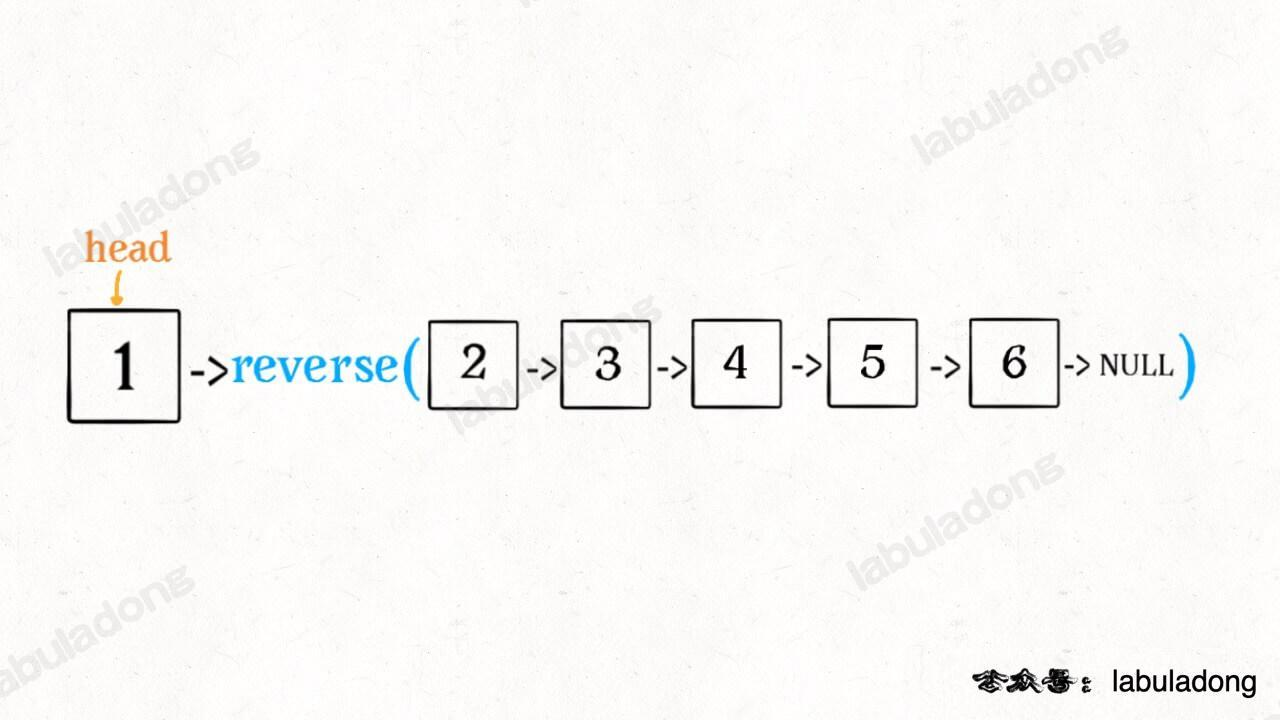
我们会得到这样的状态:
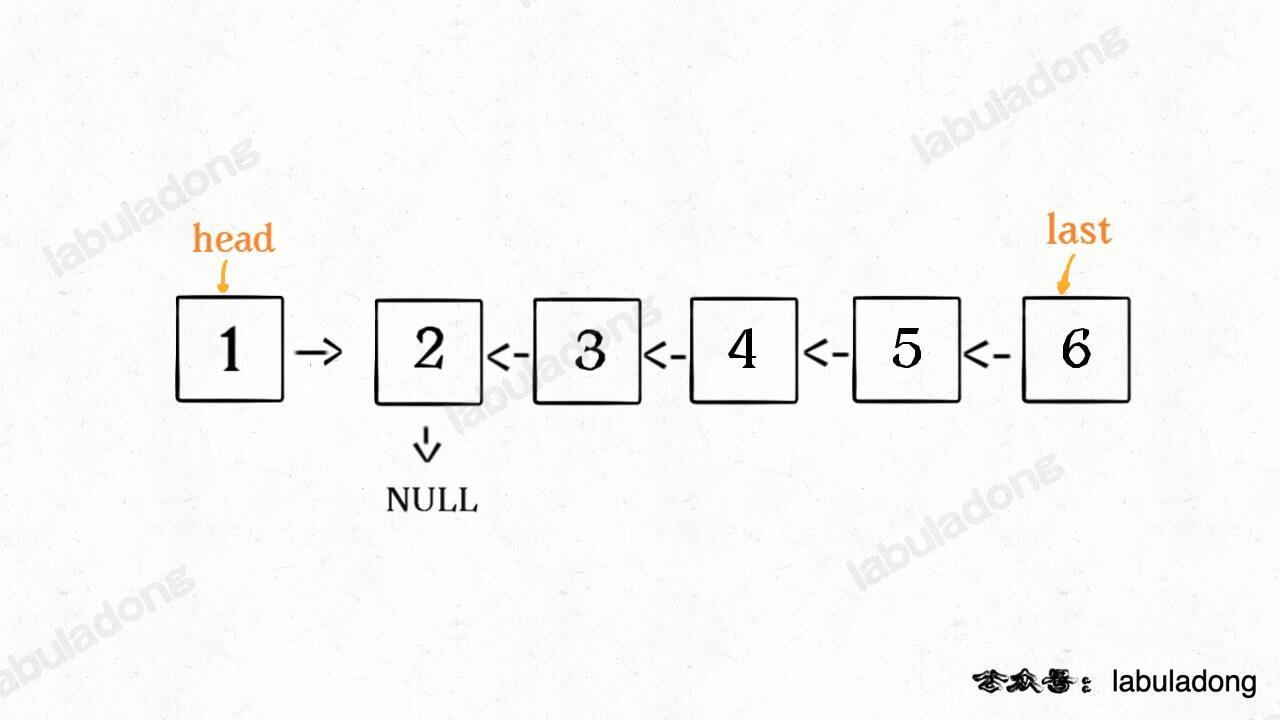
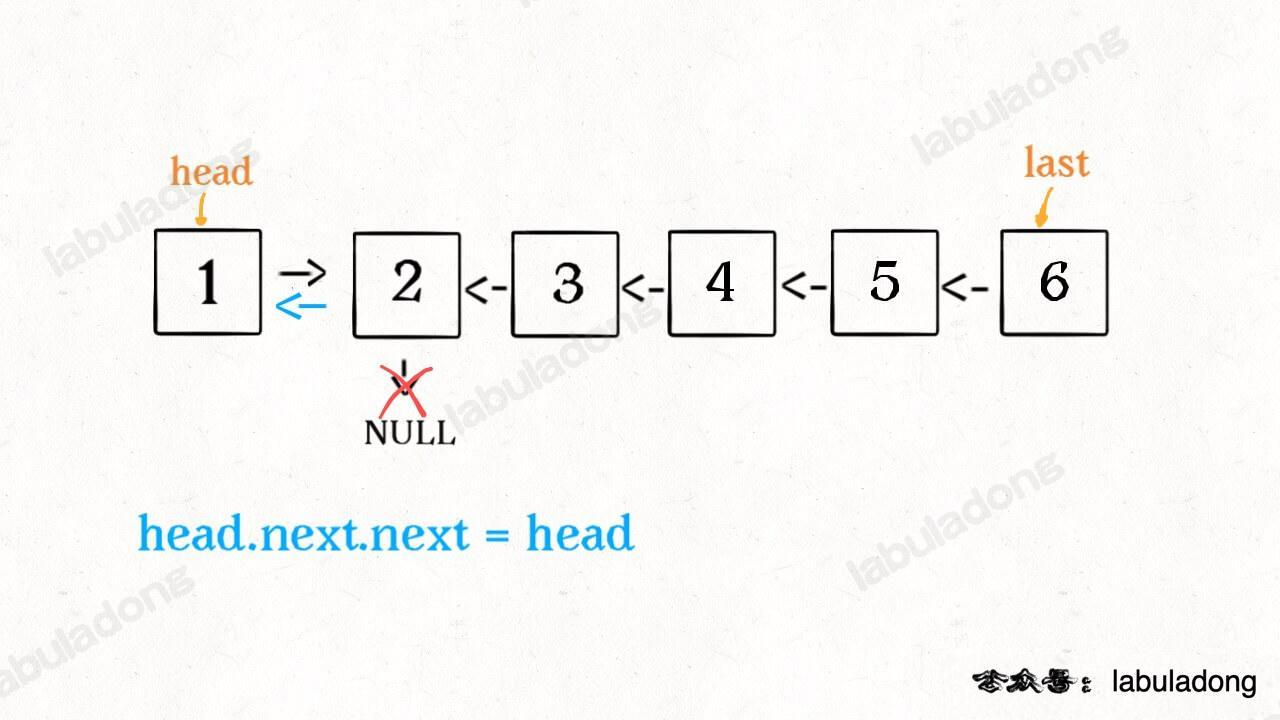
现在就只有 head 节点的指向不对了,head 应该指向 null,而2应该指向1
所以我们需要
head.next.next = head.next // 将 2 指向 head
head.next = null // 将 head 指向 null
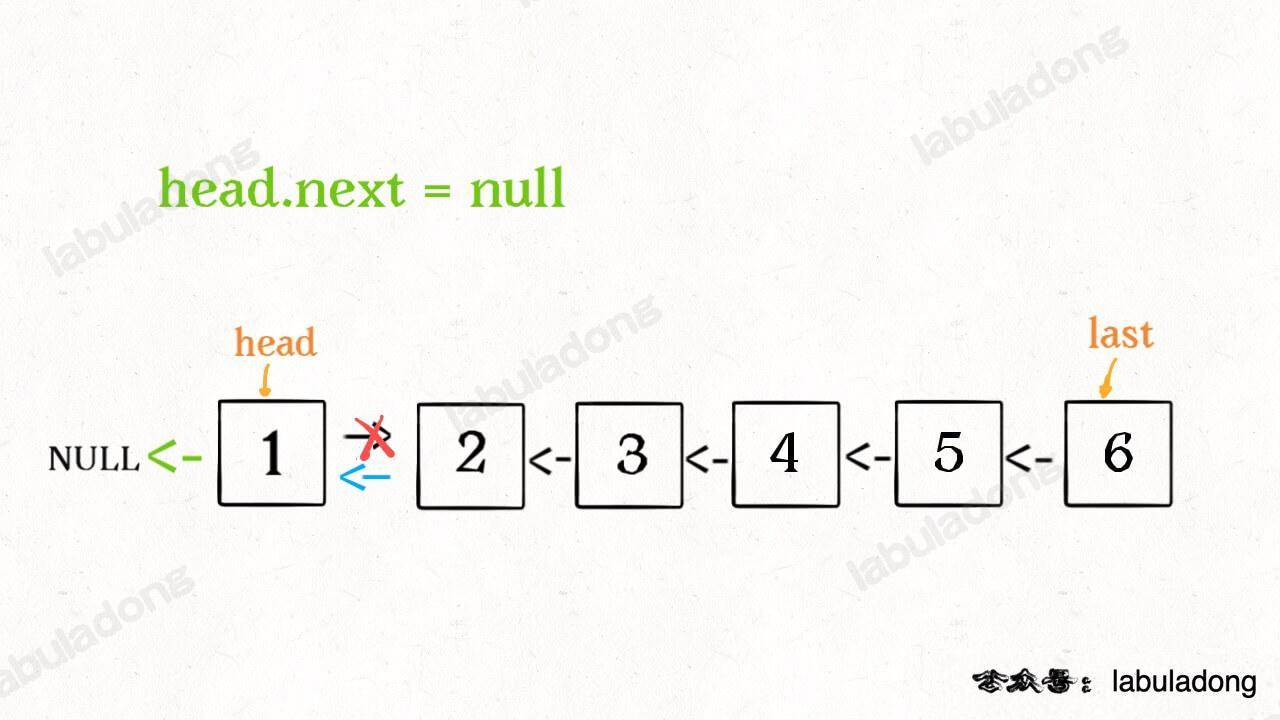
链表成功反转
清楚了递归过程之后,终止条件也很容易想到了,就是head.next == null的情况,即到了最后一个节点,直接返回该节点即可
var reverseList = function (head) {
// head == null 处理输入数据为 null 的情况
// head.next == null 是递归终止条件
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head
}
const last = reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next = head
head.next = null
return last
}
迭代
我们的目的是不断地让当前节点指向前一个节点(头结点指向null)
初始状态
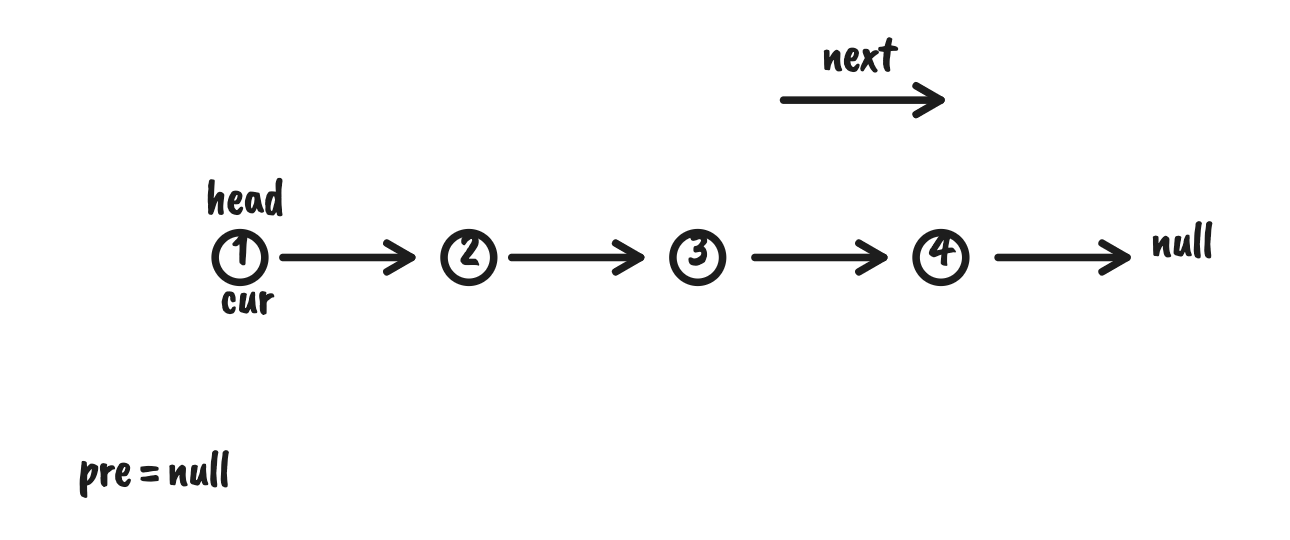
迭代过程
cur 指向 pre 后,pre 和 cur 的位置不断前移,最后返回观察图,应该返回 pre
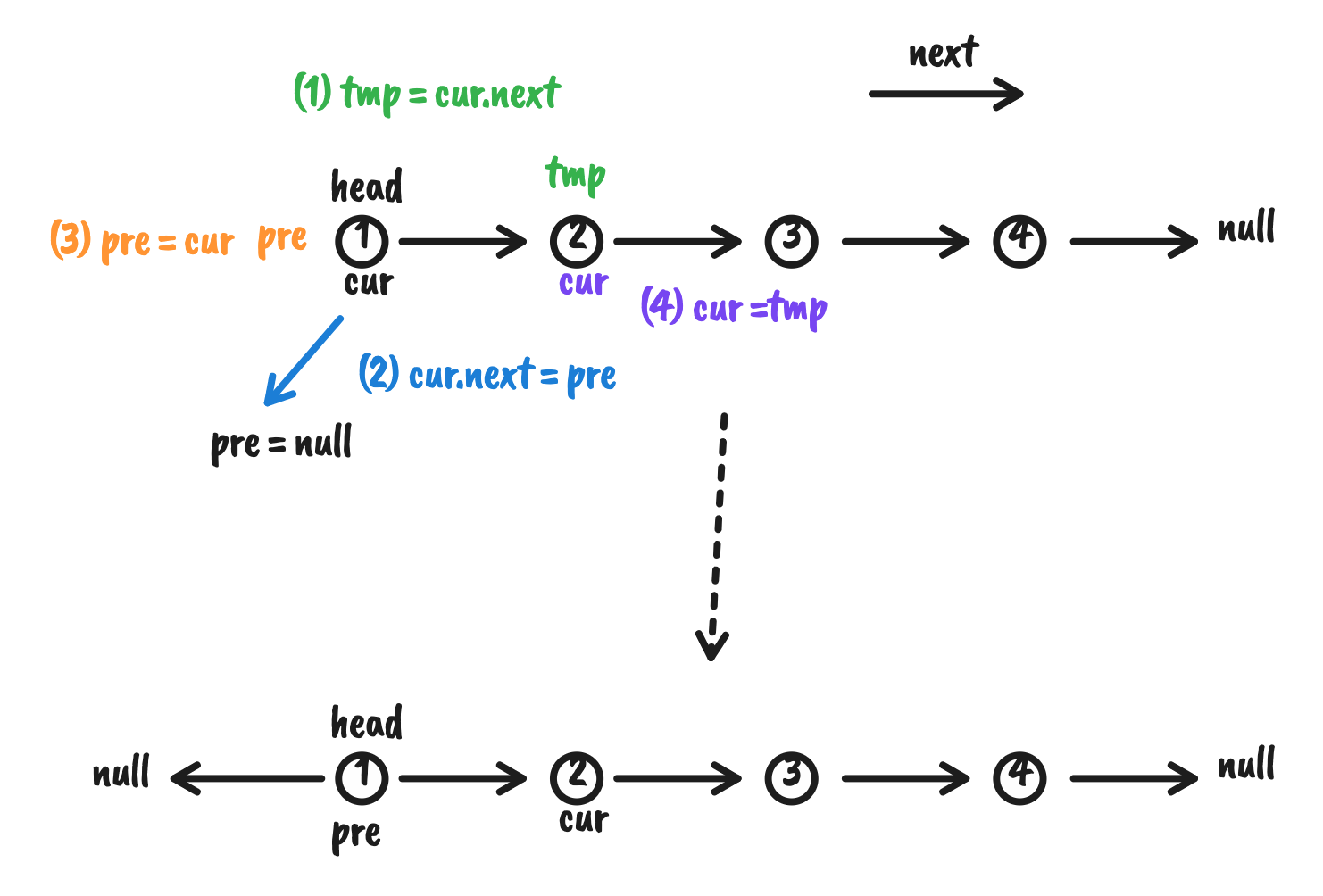
var reverseList = function (head) {
let pre = null
let cur = head
while (cur) {
const tmp = cur.next
// 当前节点指向前一个节点
cur.next = pre
// 位置前移
pre = cur
cur = tmp
}
return pre
}
剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第 k 个节点
用两个指针,它们之间相隔k个距离,那么当前面的指针到达末尾,后面的指针就正好指向倒数第 k 个节点
var getKthFromEnd = function (head, k) {
let p1 = head
let p2 = head
while (k && p2) {
p2 = p2.next
k--
}
while (p2) {
p1 = p1.next
p2 = p2.next
}
return p1
}
21. 合并两个有序链表
var mergeTwoLists = function (list1, list2) {
let p1 = list1
let p2 = list2
const head = new ListNode()
let p = head
while (p1 && p2) {
if (p1.val <= p2.val) {
p.next = p1
p1 = p1.next
} else {
p.next = p2
p2 = p2.next
}
p = p.next
}
p.next = p1 ? p1 : p2
return head.next
}
160. 相交链表
思路就是:我吹过你吹过的晚风
设置两个指针,分别指向两个链表的头节点,同时移动,到末尾之后就重新指向另一个链表的头节点,直到两个指针指向的节点相等(包括同时为null)
var getIntersectionNode = function (headA, headB) {
if (headA === null || headB === null) return null
let p1 = headA,
p2 = headB
while (p1 !== p2) {
p1 = p1 === null ? headB : p1.next
p2 = p2 === null ? headA : p2.next
}
return p1
}
字符串
5. 最长回文子串
双指针
两个指针从中心开始扩散寻找回文串,因为需要考虑回文串长度的奇偶情况,所以需要两个指针,代表回文串的中心
注意palindrome函数返回回文串时,l 和 r 已经越界了,需要向前收缩一步返回,即s.substring(l + 1, r)
var longestPalindrome = function (s) {
let res = ''
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
const s1 = palindrome(s, i, i) // 回文串长度为奇数,中心只有一个
const s2 = palindrome(s, i, i + 1) // 回文串长度为偶数,中心有两个
res = res.length > s1.length ? res : s1
res = res.length > s2.length ? res : s2
}
return res
}
function palindrome(s, l, r) {
while (l >= 0 && r < s.length && s[l] === s[r]) {
l--
r++
}
return s.substring(l + 1, r)
}
20. 有效的括号
这道题我们可以用栈来解决,当我们遇到左括号([、{、()时,就把它们加入栈,当遇到配对的右括号的时候,把它们出栈。最后如果栈为空的话,说明括号就是有效的。
当然有些过程我们可以优化一下,比如用 map 保存左右括号方便查找,当我们遇到一个不配对的右括号的时候,直接返回 false。
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValid = function (s) {
const map = {
')': '(',
'}': '{',
']': '[',
}
const stack = []
for (const char of s) {
if (map[char]) {
const c = stack.pop()
if (c !== map[char]) return false
} else {
stack.push(char)
}
}
return !stack.length
}
165. 比较版本号
分割 + 解析
版本号通过.分割,我们可以通过split将版本号分成一个一个的块,长度不足的可以在后面补0
之后比较每个块的数字就可以
/**
* @param {string} version1
* @param {string} version2
* @return {number}
*/
var compareVersion = function (version1, version2) {
const v1 = version1.split('.')
const v2 = version2.split('.')
let i = 0
while (i < v1.length || i < v2.length) {
const n1 = v1[i] ? parseInt(v1[i]) : 0
const n2 = v2[i] ? parseInt(v2[i]) : 0
if (n1 > n2) {
return 1
}
if (n1 < n2) {
return -1
}
i++
}
return 0
}
数组
1. 两数之和
哈希表
我们可以在遍历数组的时候使用map将nums[i]和下标i存下来,当遇到map中有值为target - nums[i]的键后就返回target - nums[i]的值和i组成的数组
var twoSum = function (nums, target) {
const map = new Map()
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (map.has(target - nums[i])) {
return [i, map.get(nums[i])]
}
map.set(nums[i], i)
}
}
15. 三数之和
对于这道题,我门可以先固定一个数,从而转为两数之和问题,且这题需要的是元素而不是下标,所以可以采取排序+双指针的方式来接解题
主要的流程如下:
- 遍历整个数组,每次固定一个数
- 然后使用两个指针分别指向
i+1和len-1,看这两个指针指向的数和之前固定的数的和是否为 0- 如果为 0,那么就将这三个元素加入到
ans,两个指着分别分别向左向右移动 - 如果小于 0,说明结果小了,那么就移动左指针
- 如果大于 0,说明结果打了,那么就移动右指针
- 如果为 0,那么就将这三个元素加入到
- 遍历完成后就可以返回
ans数组
这里需要考虑到一个问题就是去重,我们不做处理的话,很有可能会有重复的组被加入结果。
因为数组是经过排序的,那么相等的数就会在一起,那么遇到一样的数的时候,后面直接跳过。
var threeSum = function (nums) {
const len = nums.length
const ans = []
if (len < 3) return []
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b)
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (nums[i] > 0) break // 第一个数(最小的)大于 0 了,结果不可能为 0 了
if (i > 0 && nums[i] === nums[i - 1]) continue // 去重
let l = i + 1
let r = len - 1
while (l < r) {
const sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]
if (sum < 0) {
l++
} else if (sum > 0) {
r--
} else {
ans.push([nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]])
while (l < r && nums[l] === nums[l + 1]) l++ // 去重
while (l < r && nums[r] === nums[r - 1]) r-- // 去重
l++
r--
}
}
}
return ans
}
88. 合并两个有序数组
逆向双指针
因为nums1后面为空,可以直接覆盖,所以我们可以设置两个指针在两个数组最后(即nums1的指针在m-1,nums2的指针在n-1),从后向前遍历,将较大的元素放到 nums1 的最后面
var merge = function (nums1, m, nums2, n) {
let p1 = m - 1,
p2 = n - 1
let tail = m + n - 1
while (tail >= 0) {
if (p1 < 0) {
nums1[tail--] = nums2[p2--]
} else if (p2 < 0) {
nums1[tail--] = nums1[p1--]
} else {
nums1[tail--] = nums1[p1] >= nums2[p2] ? nums1[p1--] : nums2[p2--]
}
}
}
215. 数组中的第 K 个最大元素
我们要找到数组的第 K 大元素,首先想到要对数组进行排序,那有没有一种排序方法可以一遍排序,一遍让我们知道元素是第几大的元素呢?那就是快速排序
快速排序会确定一个pivot,排序一轮后,它左边的值都小于它,它右边的值都大于它,那么它的大小顺序就是它的下标。
这里需要注意:第 K 大元素的下标是nums.length - k,第一大元素是排序后的最后一个元素。
var findKthLargest = function (nums, k) {
const target = nums.length - k // 转换一下,第 k 大元素的下标是 len - k
let low = 0
let high = nums.length - 1
while (true) {
const index = partition(nums, low, high)
if (index === target) {
return nums[target]
} else if (index < target) {
low = index + 1
} else {
high = index - 1
}
}
}
function partition(nums, low, high) {
const mid = (low + high) >> 1
swap(nums, low, mid)
const start = low
const pivot = nums[low]
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && nums[high] >= pivot) high--
while (low < high && nums[low] <= pivot) low++
swap(nums, low, high)
}
return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val)
}
56. 合并区间
先排序
然后将最开始的区间加入res,之后的每个区间与res的最后一个区间的lastEnd值比较:
- 如果当前区间的
curStart > lastEnd,,说明这两个区间不能合并,将该区间加入res - 否则,说明两区间可以合并,选择
lastEnd和curEnd中的最大值作为新的结尾(因为要考虑前一个区间完全包含当前区间的情况)
var merge = function (intervals) {
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0])
const res = [intervals[0]]
for (let i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
const lastEnd = res[res.length - 1][1]
const [curStart, curEnd] = intervals[i]
if (curStart > lastEnd) {
res.push(intervals[i])
} else {
res[res.length - 1][1] = Math.max(curEnd, lastEnd)
}
}
return res
}
回溯
模板
result = []
def backtrack(路径, 选择列表):
if 满足结束条件:
result.add(路径)
return
for 选择 in 选择列表:
做选择
backtrack(路径, 选择列表)
撤销选择
46. 全排列
DFS
dfs函数有三个参数,分别是path保存遍历的路径,nums原数组,ans结果
回溯终止条件是 path 的长度和 nums 的长度相等,就可以将 path 加入 ans,需要注意的是需要用slice()获得 path 的深拷贝,避免获取的是 path 的引用
var permute = function (nums) {
const res = []
nums.forEach(n => dfs(res, nums, [n], [n]))
return res
}
function dfs(res, nums, path) {
if (path.length === nums.length) {
res.push(path.slice())
return
}
nums.forEach(n => {
if (!path.includes(n)) {
path.push(n)
dfs(res, nums, path)
path.pop()
}
})
}
22. 括号生成
var generateParenthesis = function (n) {
const res = []
dfs(res, n, [], 0)
return res
}
function dfs(res, n, path, left) {
if (path.length === n * 2) {
res.push(path.join(''))
return
}
if (left < n) {
path.push('(')
dfs(res, n, path.slice(), left + 1)
path.pop()
}
if (path.length - left < left) {
path.push(')')
dfs(res, n, path.slice(), left)
path.pop()
}
}
动态规划
53. 最大子序和
动态规划
我们定义 dp[n] 为以 nums[n] 结尾的子数组最大和,我们可以想到 dp[n] 的最大值应该等于 dp[n - 1] 考虑加不加上 nums[n],所以我们比较dp[n - 1] + nums[n]和nums[n] 的大小,其中较大的为 dp[n] 的值
那么有以下状态转移公式:
初始值为 dp[0] = nums[0]
再用一个变量 max 记录一下 dp[n] 中的最大值
var maxSubArray = function (nums) {
let max = nums[0]
const dp = []
dp[0] = nums[0]
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i])
max = Math.max(max, dp[i])
}
return max
}
300. 最长递增子序列
动态规划
- 定义状态:
dp[i] 表示:以 nums[i] 结尾的最长上升子序列的长度
- 状态转移方程:
如果一个较大的数接在较小的数后面,就会形成一个更长的子序列。只要 nums[i] 大于在它位置之前的某个数,那么 nums[i] 就可以接在这个数后面形成一个更长的上升子序列。所以我们找到符合nums[i] > nums[j]的dp[j]的最大值就可以了
- 初始化:
dp[i] = 1,每个字符都可以认为是长度
var lengthOfLIS = function (nums) {
const dp = new Array(nums.length).fill(1)
let max = 1
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1)
}
}
max = Math.max(max, dp[i])
}
return max
}
322. 零钱兑换
状态定义:dp[i]表示组成金额i需要最少的硬币个数
base case:dp[0] = 0
状态转移:dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - coin] + 1, dp[i])
当i - coin >= 0时,说明dp[i]可以由dp[i - coin]加coin这一个硬币组成
var coinChange = function (coins, amount) {
const dp = new Array(amount + 1).fill(Infinity)
dp[0] = 0
for (let i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) {
for (const coin of coins) {
if (i - coin < 0) continue
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - coin] + 1, dp[i])
}
}
return dp[amount] === Infinity ? -1 : dp[amount]
}
718. 最长重复子数组
var findLength = function (nums1, nums2) {
const m = nums1.length
const n = nums2.length
const dp = new Array(m + 1).fill(0).map(e => new Array(n + 1).fill(0))
let max = 0
for (let i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
// nums1[i-1] != nums2[j-1]的情况,初始化时已包括了
if (nums1[i - 1] === nums2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
}
max = Math.max(dp[i][j], max)
}
}
return max
}
64. 最小路径和
var minPathSum = function (grid) {
const m = grid.length
const n = grid[0].length
const dp = new Array(m).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill(Infinity))
dp[0][0] = grid[0][0]
for (let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + grid[i][0]
}
for (let j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1] + grid[0][j]
}
for (let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j]
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
}
排序
快速排序
var sortArray = function (nums) {
quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1)
return nums
}
function quickSort(nums, low, high) {
if (low >= high) return
const pivot = partition(nums, low, high)
quickSort(nums, low, pivot - 1)
quickSort(nums, pivot + 1, high)
}
function partition(nums, low, high) {
const mid = (low + high) >> 1
swap(nums, mid, low)
const pivot = nums[low]
const start = low
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && nums[high] >= pivot) high--
while (low < high && nums[low] <= pivot) low++
swap(nums, low, high)
}
swap(nums, start, low)
return low
}
function swap(nums, i, j) {
;[nums[i], nums[j]] = [nums[j], nums[i]]
}
贪心
121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
因为股票就买卖一次,那么贪心的想法很自然就是取最左最小值,取最右最大值,那么得到的差值就是最大利润。
var maxProfit = function (prices) {
let low = Infinity
let max = 0
for (let i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
low = Math.min(low, prices[i])
max = Math.max(max, prices[i] - low)
}
return max
}
滑动窗口
框架
let left = 0, right = 0;
while (right < s.length) {
// 增大窗口
window.add(s[right]);
right++;
while (window needs shrink) {
// 缩小窗口
window.remove(s[left]);
left++;
}
}
3. 无重复字符的最长子串
双指针实现滑动窗口
遍历字符串,用 map 来存子串的字符,key 是 字符,value 是字符的个数,右指针每拿到一个字符 c ,就将 map[c] 的值加一,那么当 map[c] > 1 时,说明已经有字符重复,需要将左指针向右移动,左指针拿到的的字符 d,将 map[d] 的值减一,直到 map[c] == 1,即我们已经删除了重复的字符,这时候就可以记录最大长度。
需要注意的是,map 没有初始化,直接 map[c]++ 会有问题,我们需要判断一下 map[c] 为 undefined 的情况
map[c] = map[c] === undefined ? 1 : map[c] + 1
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {number}
*/
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function (s) {
const map = {}
let left = 0,
right = 0
let max = 0
while (right < s.length) {
const c = s[right]
right++
map[c] = map[c] === undefined ? 1 : map[c] + 1
while (map[c] > 1) {
const d = s[left]
left++
map[d]--
}
max = Math.max(max, right - left)
}
return max
}
209. 长度最小的子数组
我们确定好缩小窗口的条件是sum >= target,然后套用框架就行了
这里需要注意的是计算长度的时候是用r - l,因为这时候j已经是在下一个索引了不需加 1
var minSubArrayLen = function (target, nums) {
const len = nums.length
let l = (r = 0)
let res = len + 1 // 子数组最大不会超过自身
while (r < len) {
// 窗口增大
sum += nums[r++]
// 窗口缩小
while (sum >= target) {
// r始终为开区间 [l, r)
res = Math.min(res, r - l)
sum -= nums[l++]
}
}
return res > len ? 0 : res
}
栈
155. 最小栈
主要考点在常数时间内检索到最小元素,这就要求我们要将最小的元素保存下来
我们可以使用两个栈来实现,一个栈正常保存元素,另一个栈专门用来保存最小元素
关键在于push操作,我们需要判断保存最小元素的栈的入栈值:
如果最小栈为空时,那么入栈的就是val
如果最小栈不为空,需要判断val和最小栈栈顶元素的大小,入栈val和最小栈栈顶元素中小的元素
这样保证了两个栈元素数量相同,方便pop操作
class MinStack {
constructor() {
this.stack = []
this.minStack = []
}
push(val) {
this.stack.push(val)
if (this.minStack.length === 0 || val <= this.minStack[this.minStack.length - 1]) {
this.minStack.push(val)
} else {
this.minStack.push(this.minStack[this.minStack.length - 1])
}
}
pop() {
this.stack.pop()
this.minStack.pop()
}
top() {
return this.stack[this.stack.length - 1]
}
getMin() {
return this.minStack[this.minStack.length - 1]
}
}
146. LRU 缓存机制
哈希链表
唯一需要注意的是,put操作时,如果容量满了需要删除最不常用元素时,先删map中的key(因为需要this.dummyTail.prev.key拿到),然后再删链表中的this.dummyTail.prev节点
class LRUCache {
constructor(capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity
this.map = new Map()
this.dummyHead = new ListNode()
this.dummyTail = new ListNode()
this.dummyHead.next = this.dummyTail
this.dummyTail.prev = this.dummyHead
}
get(key) {
if (!this.map.has(key)) {
return -1
} else {
const node = this.map.get(key)
this.moveToHead(node)
return node.value
}
}
put(key, value) {
if (this.map.has(key)) {
const node = this.map.get(key)
this.moveToHead(node)
node.value = value
} else {
if (this.capacity === this.map.size) {
this.map.delete(this.dummyTail.prev.key)
this.removeNode(this.dummyTail.prev)
}
const node = new ListNode(key, value)
this.addToHead(node)
this.map.set(key, node)
}
}
removeNode(node) {
node.prev.next = node.next
node.next.prev = node.prev
}
addToHead(node) {
node.prev = this.dummyHead
node.next = this.dummyHead.next
this.dummyHead.next.prev = node
this.dummyHead.next = node
}
moveToHead(node) {
this.removeNode(node)
this.addToHead(node)
}
}
class ListNode {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key
this.value = value
this.next = null
this.prev = null
}
}
415. 字符串相加
双指针模拟
用指针模拟从后向前加,没有的位补零。
需要注意的是两个数取完了,但最后 carry 不为 0 时,需要多循环一次,因为这是 carry 在下一位
var addStrings = function (num1, num2) {
let i = num1.length - 1,
j = num2.length - 1
let ans = []
let carry = 0
// 别忘了 carry
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || carry) {
const n1 = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i) - '0' : 0
const n2 = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j) - '0' : 0
const sum = n1 + n2 + carry
carry = Math.floor(sum / 10)
ans.push(sum % 10)
i--
j--
}
return ans.reverse().join('')
}
70. 爬楼梯
动态规划
因为我们一次可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶,那么爬到第 n+2 阶台阶的方法数就等于爬到第 n+1 阶台阶的方法数和爬到第 n 阶台阶的方法数之和
我们定义 dp[n] 为爬到第 n 阶台阶的方法数,我们可以推出状态转移公式:
初始状态为 dp[1] = 1,dp[2] = 2
var climbStairs = function (n) {
const dp = []
dp[1] = 1
dp[2] = 2
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]
}
return dp[n]
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
BFS
用一个数组保存每一层的节点,如果这个数组中没有元素,那么就终止遍历
var levelOrder = function (root) {
if (root === null) return []
const ans = []
bfs([root], ans)
return ans
}
const bfs = (list, ans) => {
ans.push(list.map(e => e.val))
const nextList = []
list.forEach(e => {
e.left !== null && nextList.push(e.left)
e.right !== null && nextList.push(e.right)
})
if (!nextList.length) return
bfs(nextList, ans)
}
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
方法一 递归
var inorderTraversal = function (root) {
const res = []
const inorder = root => {
if (!root) {
return
}
inorder(root.left)
res.push(root.val)
inorder(root.right)
}
inorder(root)
return res
}
方法二 迭代
var inorderTraversal = function (root) {
const res = []
const stk = []
while (root || stk.length) {
while (root) {
stk.push(root)
root = root.left
}
root = stk.pop()
res.push(root.val)
root = root.right
}
return res
}
剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列
动态规划
状态定义:dp[i]表示斐波那契数列第 i 项的值
状态转移方程:dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]) % 1000000007 (本题要求取模)
初始状态:dp = [0,1]
输出:dp[n]
const fib = n => {
const dp = [0, 1]
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]) % 1000000007
}
return dp[n]
}
322. 零钱兑换
动态规划
状态定义:dp[i]表示凑齐 i 元所需最少的硬币个数
状态转移方程:dp[i] = min(dp[i],dp[i - coin] + 1) ,其中 coin 为 coins 中的每个元素
初始状态:dp[0] = 0
输出:如果没有能组成总金额的话输出 -1,否则输出dp[amount]
var coinChange = function (coins, amount) {
const dp = new Array(amount + 1).fill(Infinity)
dp[0] = 0
for (let i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (let coin of coins) {
if (coin <= i) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coin] + 1)
}
}
}
return dp[amount] === Infinity ? -1 : dp[amount]
}
56. 合并区间
先排序,后看区间
我们首先将intervals数组根据start升序排序来保证每个区间是连续的,接着用ans数组来保存结果。
首先将排序后的数组sorted的第一个区间放入ans中,之后的sorted每个区间与ans的最后一个区间比较:
- 如果当前区间的
curEnd小于lastEnd,说明区间不重合,直接将当前区间加入ans - 否则区间重合,将
ans的最后一个区间的end更新为curEnd和lastEnd之中较大的值
var merge = function (intervals) {
let ans = []
let sorted = intervals.sort((left, right) => left[0] - right[0])
ans.push(sorted[0])
for (let i = 1; i < sorted.length; i++) {
const [_, lastEnd] = ans[ans.length - 1]
const [curStart, curEnd] = sorted[i]
if (curStart > lastEnd) {
ans.push(sorted[i])
} else {
ans[ans.length - 1][1] = Math.max(lastEnd, curEnd)
}
}
return ans
}
200. 岛屿数量
网格题的 DFS 基本框架
对于这种网格的题我们可以将它想成是一个四叉树,即上、下、左、右,四个方向
遍历过程中会出现一些越界的问题,我们利用“先污染后治理”的思想来统一遍历过程,即可以超出边界,下一轮遍历再判断是否超出边界
对于二叉树来说就是节点是否为 null,而对于网格来说就是是否超出网格范围,若超出则直接返回
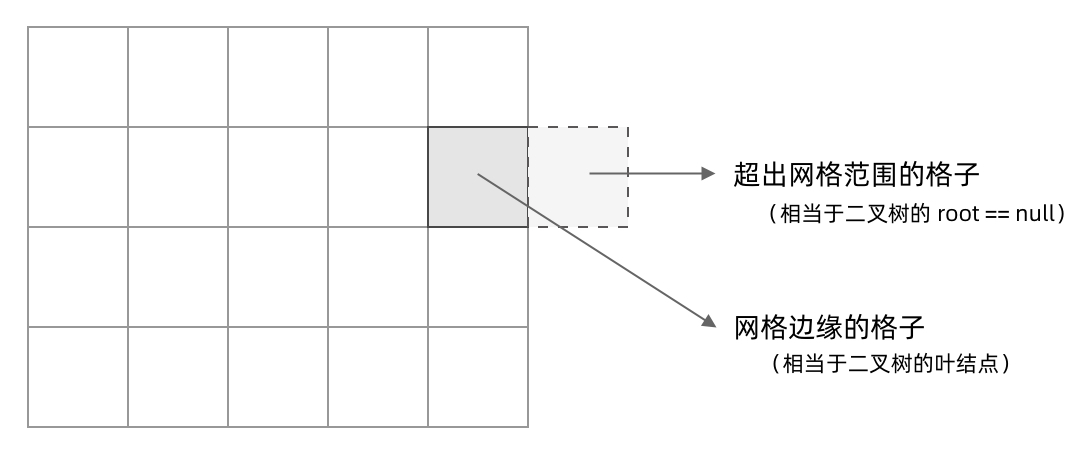
于是,我们可以建立这么一个框架
function dfs(grid, i, j) {
// 如果越界直接返回
if (!inArea(grid, i, j)) {
return
}
// 访问上下左右
dfs(grid, i + 1, j)
dfs(grid, i - 1, j)
dfs(grid, i, j + 1)
dfs(grid, i, j - 1)
}
接下来,我们还需要避免一个问题,那就是之前遍历过的点,之后就不需要遍历了,防止死循环出现,如图:
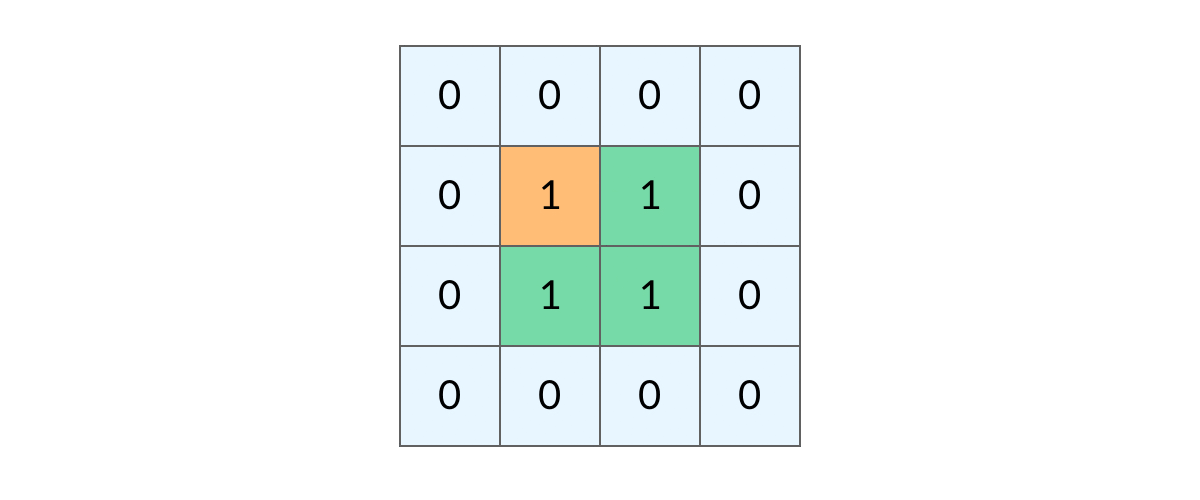
所以我们需要标记一下已经遍历过的格子
function dfs(grid, i, j) {
// 如果越界或不是未遍历过的陆地直接返回
if (!inArea(grid, i, j) || grid[i][j] != '1') {
return
}
// 标记陆地为已遍历
grid[i][j] = '2'
// 访问上下左右
dfs(grid, i + 1, j)
dfs(grid, i - 1, j)
dfs(grid, i, j + 1)
dfs(grid, i, j - 1)
}
对于本题,代码如下:
var numIslands = function (grid) {
let count = 0
for (let i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
dfs(grid, i, j)
++count
}
}
}
return count
}
function dfs(grid, i, j) {
if (!inArea(grid, i, j) || grid[i][j] != '1') {
return
}
grid[i][j] = '2'
dfs(grid, i + 1, j)
dfs(grid, i - 1, j)
dfs(grid, i, j + 1)
dfs(grid, i, j - 1)
}
function inArea(grid, i, j) {
return i >= 0 && i < grid.length && j >= 0 && j < grid[0].length
}
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
祖先:若节点 p 在节点 root 的左(右)子树中,或 p = root,则称 root 是 p 的祖先
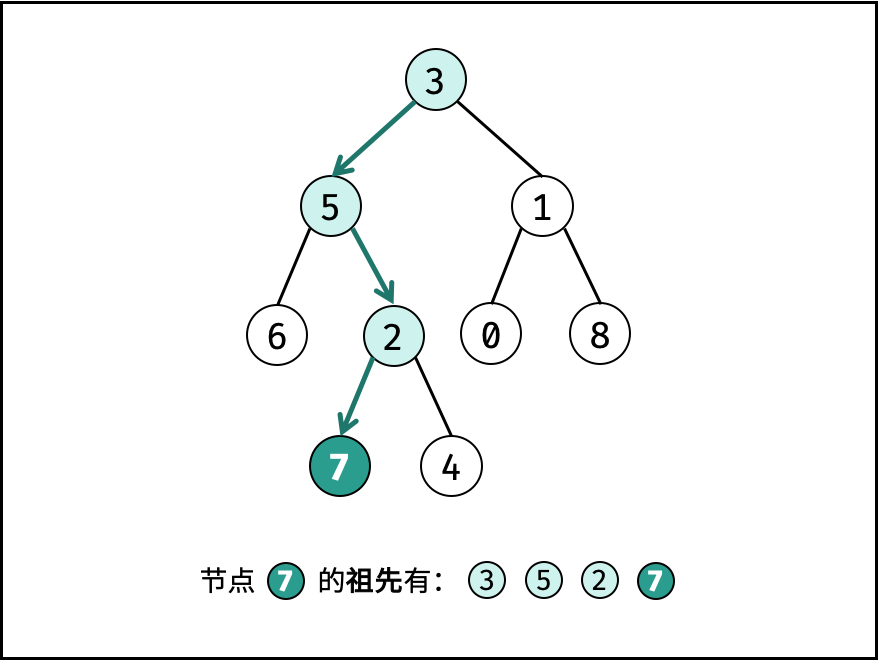
根据定义,若 root 是 p,q 的最近公共祖先,只有三种情况:
- p 和 q 在 root 的子树中,且分别在左、右子树中
- p = root,且 q 在 root 的子树中
- q = root ,且 p 在 root 的子树中
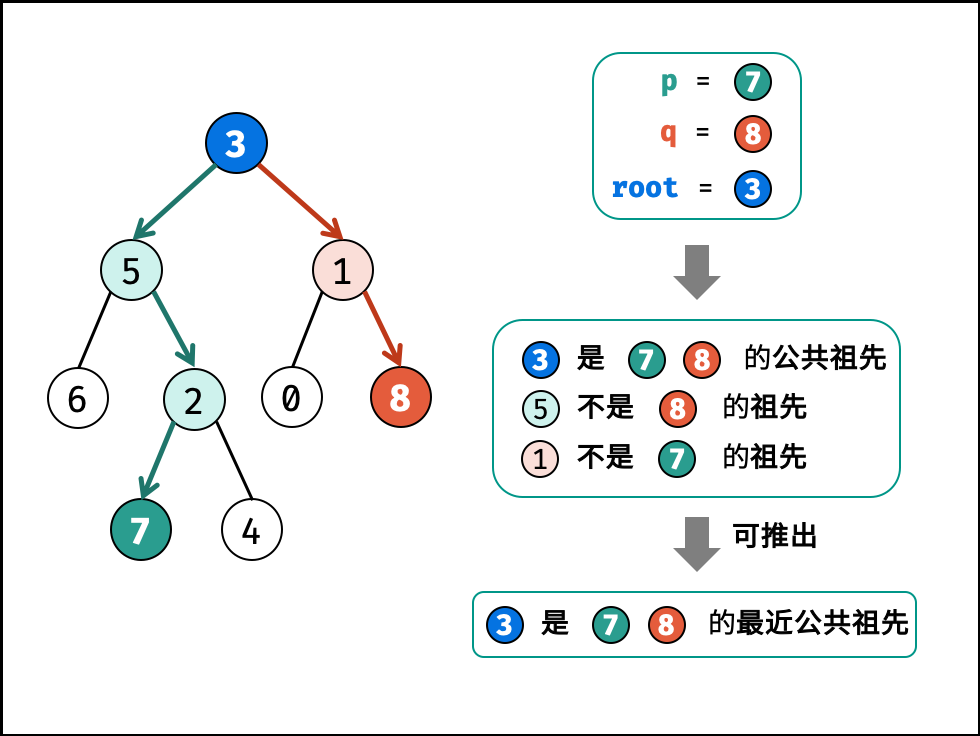
下面就来分析一下递归函数lowestCommonAncestor:
终止条件:
root == null时,返回null这是二叉树递归的常规终止条件root === p || root === q,root 本身就是 p 或 q,也就是找到了要找的节点,那么就返回root
递归状态:
分别递归左、右子树,左子树返回值为
left,右子树返回值为right函数返回值:
- 当
left和right都不为空时,那么它们一定是 p 和 q,root 就为它们的最近公共祖先(这里因为我们用的是二叉树的后序遍历,就好比从p和q出发往上走,第一次相交的节点就是这个root,即最近公共祖先) - 当
left和right都为空时,返回null - 当
left和right有一个不为空,那么就返回不为空的节点,即是返回了 p 或者 q,或是它们的最近公共祖先
- 当
var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q) {
if (root == null) return
if (root === p || root === q) return root
const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if (left && right) return root
if (!left && !right) return null
return left == null ? right : left
}